Window 11 Hardening Techiniques

Hardening Windows 11 for Compliance-Driven Environments
Hardening Windows 11 for Compliance-Driven Environments
Windows 11 introduces a security-first architecture that can be tuned to meet stringent regulatory frameworks (CMMC, CIS L1/L2, DISA STIG, ISO 27001, PCI-DSS, etc.). This guide maps the Microsoft-recommended baseline, current sector guidance (2024–2025), and practical Group Policy/Intune steps to achieve a defense-in-depth posture.
Key takeaway: combine silicon-rooted trust (TPM 2.0, Secure Boot) with virtualization-based isolation, credential protections, application control, and continuous monitoring to reduce successful attack surface by more than 2× compared with legacy Windows 10.
1 Hardware & Firmware Foundations
1.1 UEFI Secure Boot
- Keep firmware in UEFI mode; disable CSM/legacy boot.
- Verify Secure Boot ON via
msinfo32→ “Secure Boot State: ON”.
1.2 TPM 2.0
- Mandatory for Windows 11 and required for BitLocker, Credential Guard, Windows Hello, measured boot and attestation.
- Update TPM firmware regularly (CVE-2023-1017/1018 mitigations).
1.3 DMA & Boot-kit Defenses
- Enable Kernel DMA Protection in BIOS.
- Block Thunderbolt/FireWire pre-boot via UEFI or “DisableExternalDMAUnderLock”.
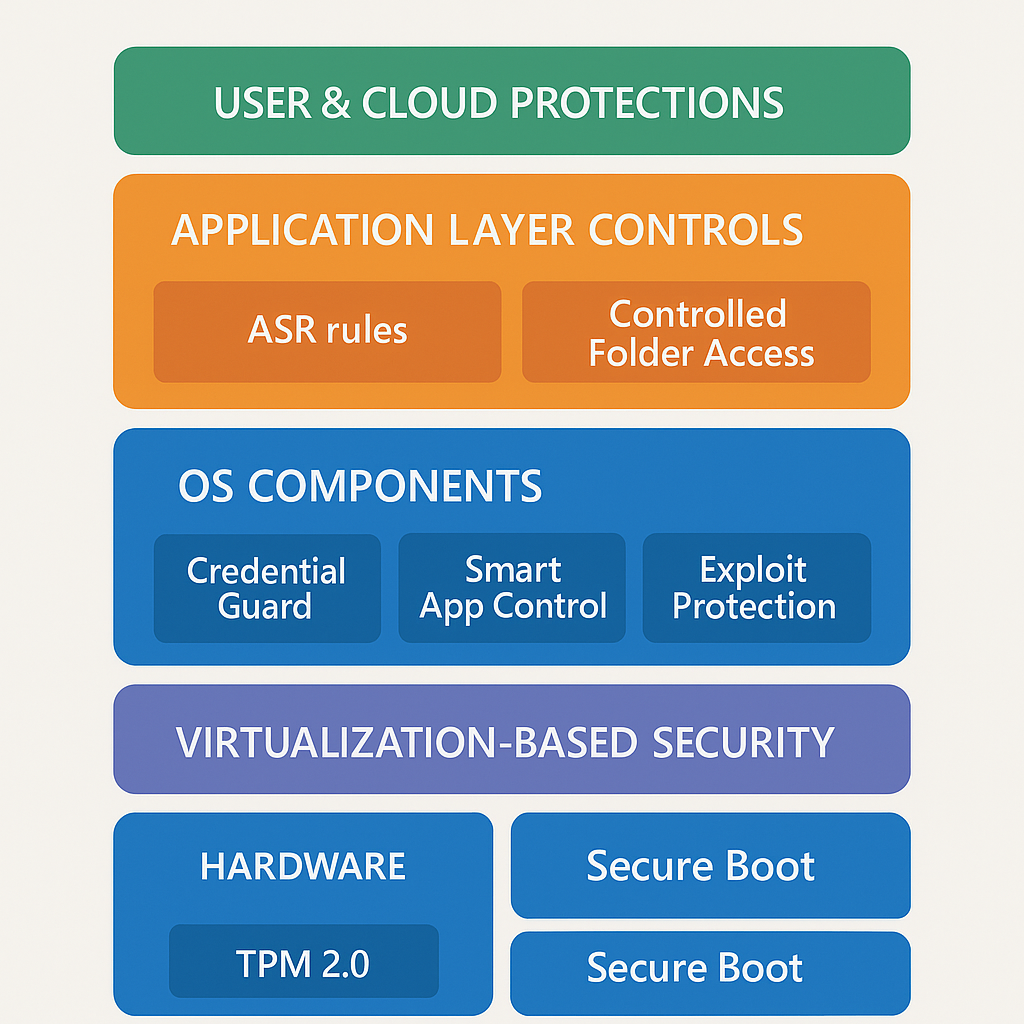
2 Virtualization-Based Security (VBS) Stack
| Control | Purpose | Configuration (GPO/Intune) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Memory Integrity (HVCI) | Stops unsigned or modified kernel code | Device Security → Core isolation → ON or GPO HypervisorEnforcedCodeIntegrity = 1 | Balanced mode shows <5% perf cost in Office workloads but up to 15% in some games; disable only on dedicated GPU rigs. |
| Credential Guard | Isolates NTLM/Kerberos secrets | GPO “Turn on VBS” → Credential Guard “Enabled with UEFI lock” | Default-enabled on 22H2+ Enterprise/Edu. Test impact on older VPN/PEAP stacks. |
| Secured-core PC settings | Enforces System Guard Secure Launch, SMM protection | OEM-supplied; verify in Device Security | Needed for FedRAMP High, DoD Cloud SRG. |
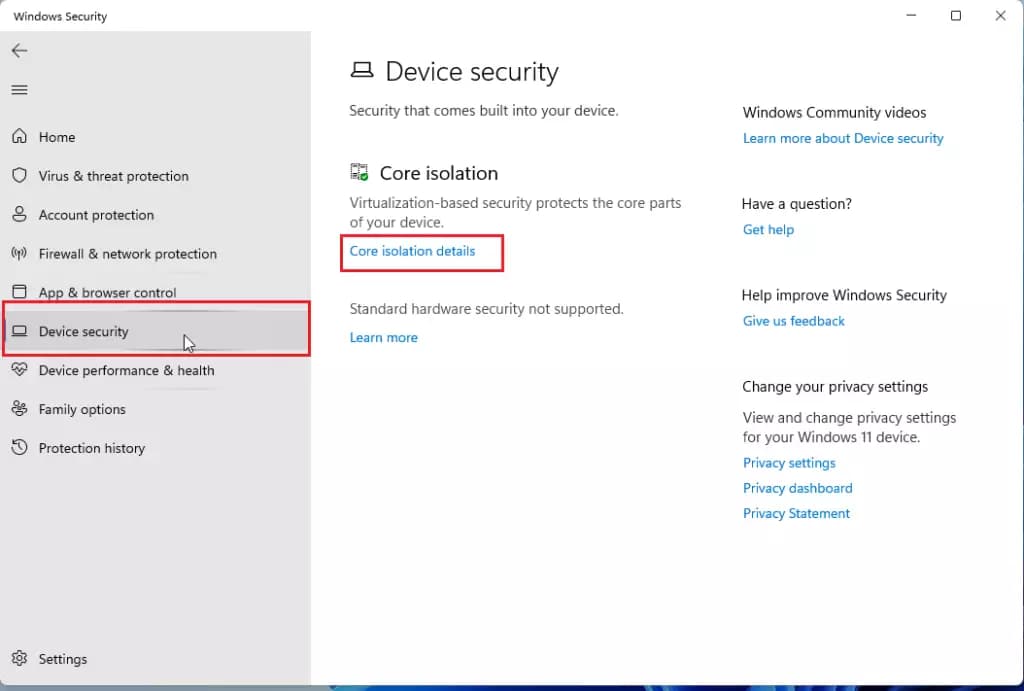
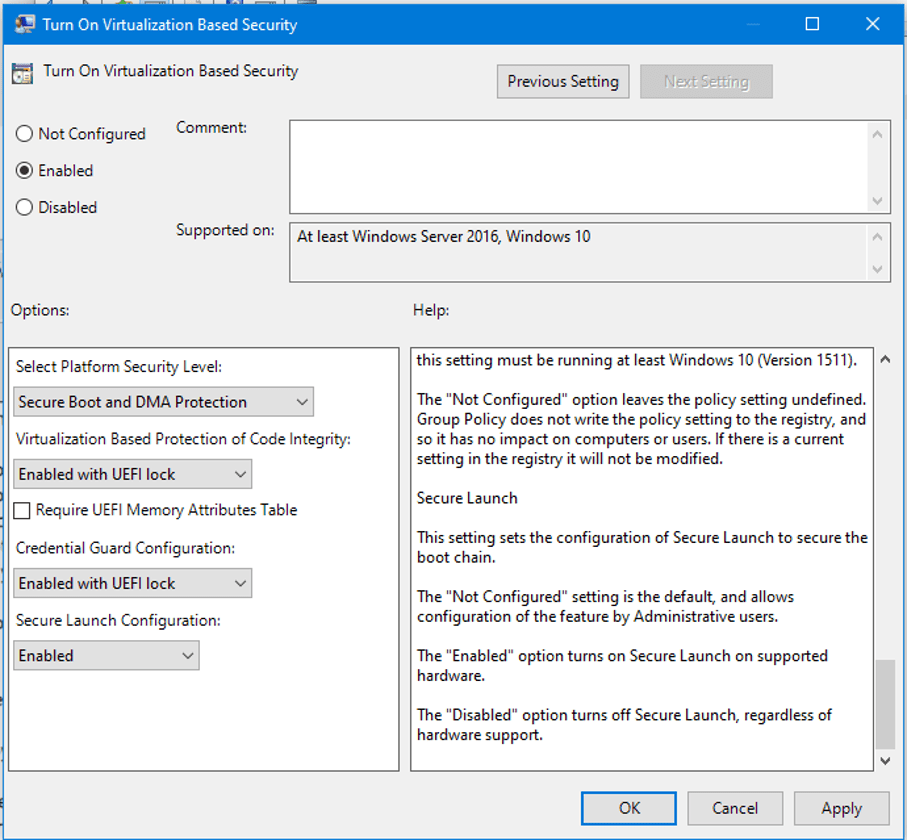
3 OS-Level Protections
3.1 Exploit Protection & Attack Surface Reduction
- Import Microsoft Baseline XML or Intune “Exploit protection” profile; include system mitigations (DEP, CFG, SEHOP, Mandatory ASLR).
- Enable all 19 ASR rules at least in Audit mode; switch high-value endpoints (finance, devops) to Block for:
- Block credential stealing from LSASS
- Block Office child-process creation
- Block vulnerable signed drivers (new July 2024 rule).
3.2 Smart App Control & Application Whitelisting
- For green-field images, keep Smart App Control in On or Evaluation mode to block unsigned/untrusted EXEs/MSIs/Scripts.
- For brown-field fleets, deploy WDAC or AppLocker policies generated from known-good baselines.
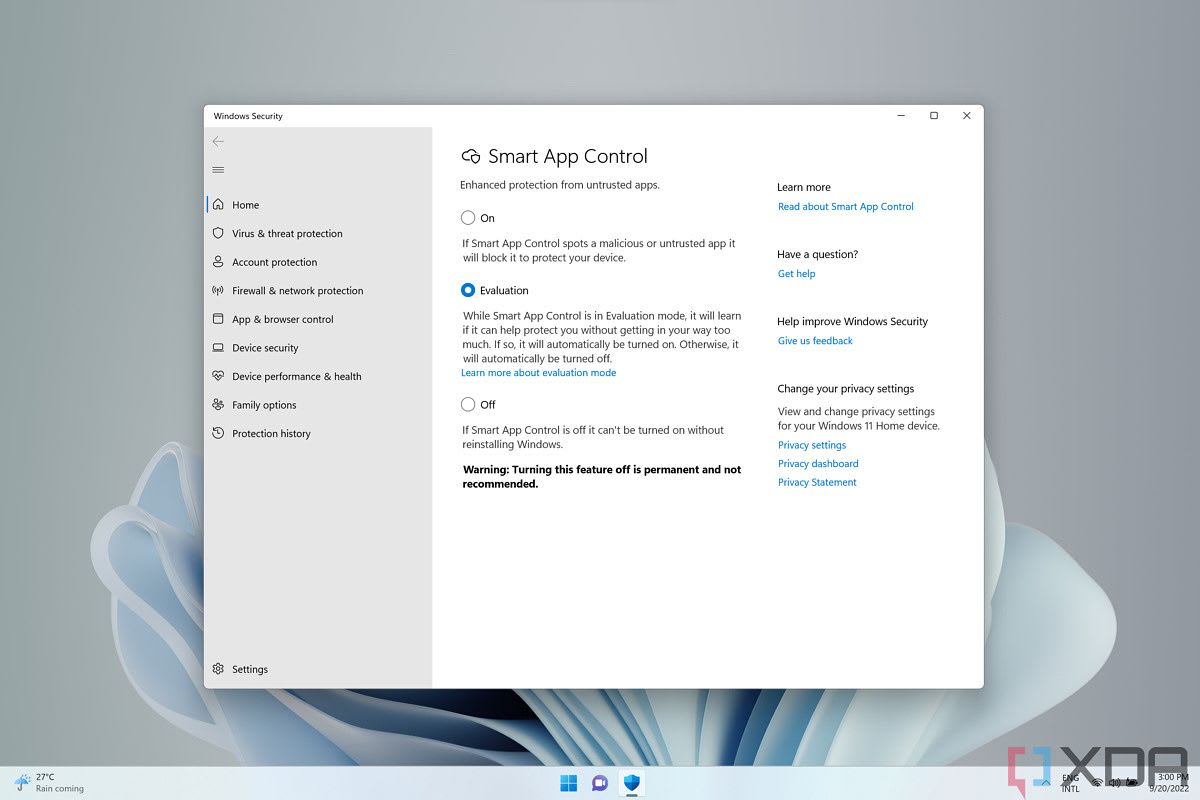
3.3 Patch & Update Cadence
- Use Windows Update for Business or WSUS with auto-install time ≤7 days; 0-day out-of-band patches ≤24 h.
- Enable driver blocklist via “Vulnerable Driver Blocklist” toggle (Windows 11 23H2+).
3.4 BitLocker & Drive Manifests
Enforce XTS-AES-256, TPM + PIN for admin laptops; store keys in Azure AD or AD DS escrow.
Require BitLocker for all fixed and removable media (Intune Endpoint Protection → Windows Encryption).
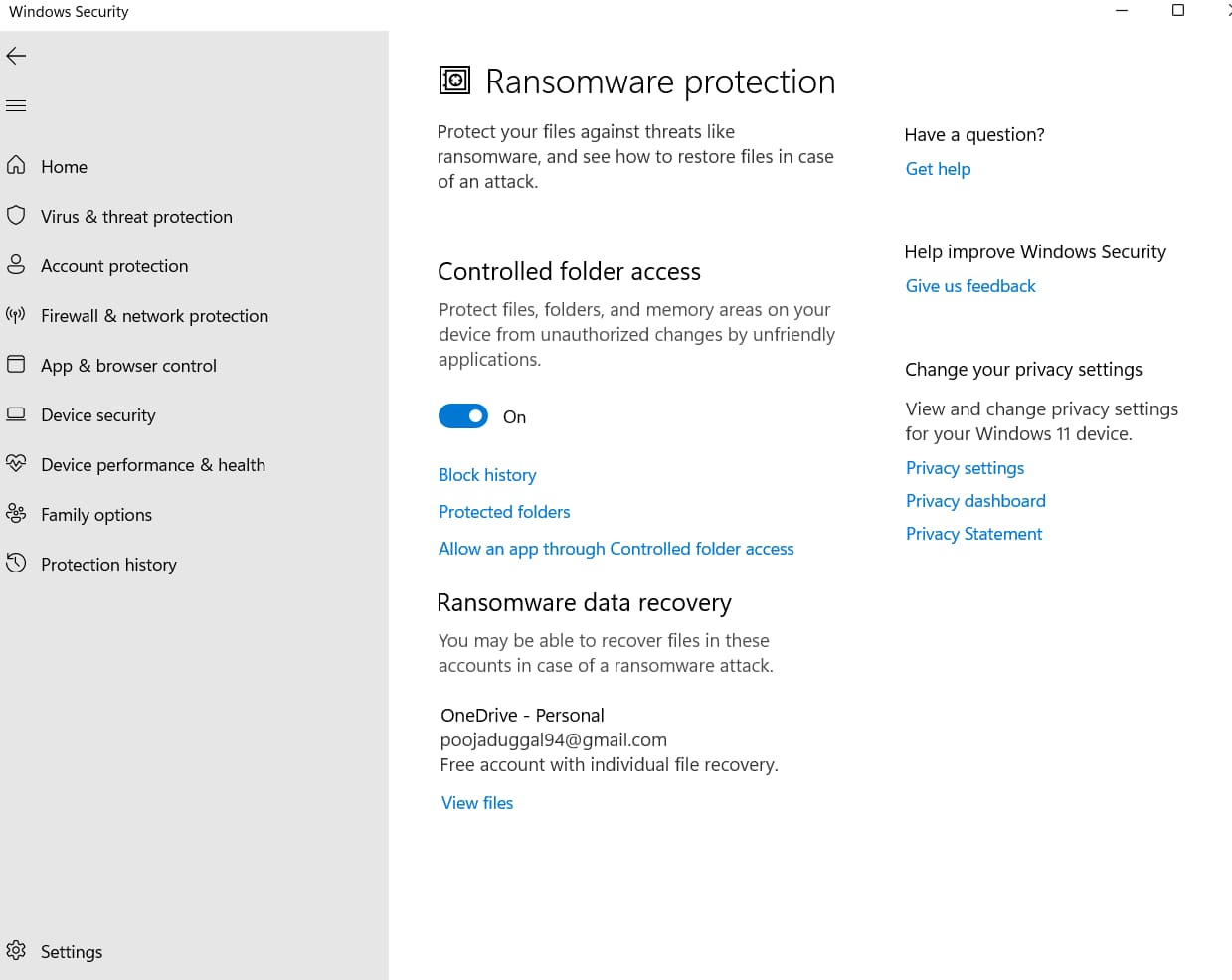
3.5 Controlled Folder Access (CFA) & Ransomware Data Recovery
- Turn CFA On; add departmental shares and project folders.
- Pair with OneDrive Known-Folder Move or server snapshots to satisfy ransomware resiliency controls (PCI-DSS 12.3, HIPAA-164.308-A7).
4 Identity & Credential Management
4.1 Local Administrator Password Solution (Windows LAPS)
Replace identical local admin passwords with randomized 30-char complex passphrases rotated ≤30 days.
Store secrets in on-prem AD or Azure AD with RBAC-scoped recovery.
Block remote use of local SAM accounts (
Apply UAC restrictions to local accounts on network logons).

4.2 Multi-Factor & Passwordless
- Enforce Windows Hello for Business or FIDO2 security keys for all privileged accounts (Admins, Developers, HelpDesk).
- Disable legacy NTLMv1; set
LMCompatibilityLevel = 5,NoLMHashvia GPO.
4.3 Account Lockout & UAC
- Lockout after 5 invalid attempts, 15-minute reset.
- UAC: “Prompt for credentials on secure desktop” for admins; “Automatically deny” for standard users.
5 Network & Firewall Policies
| Component | Hardening Action |
|---|---|
| Microsoft Defender Firewall | ON for Domain/Private/Public; outbound rules restricted to approved executables. |
| SMB | SMBv1 disabled; SMB signing required; SMB over QUIC for remote laptops. |
| WinRM | Allow only HTTPS listener with certificate; disable Remote PowerShell access for non-admins. |
| WPAD & LLMNR | Disabled to prevent NBNS spoofing. |
6 Logging, Monitoring, and Response
Forward Windows Event logs (Security, Sysmon, Microsoft-Windows-DeviceGuard, Microsoft-Windows-WDIG/WHC) to SIEM.
Enable Microsoft Defender for Endpoint sensor for EDR-level telemetry and Automated Investigation & Response (AIR).
Configure attack surface reduction reporting and exploit protection event channels to Success+Failure for audit trails (NIST 800-92).
7 Compliance-Ready Baseline Checklist
| Category | Key Setting | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Hardware | TPM 2.0 present & PCR-bound | |
| Boot | Secure Boot & Measured Boot | |
| Isolation | VBS + HVCI + Secure Launch | |
| Credentials | Credential Guard, LAPS, NTLM restrictions | |
| Apps | ASR full set, Smart App Control, WDAC | |
| Data | BitLocker XTS-AES-256, CFA | |
| Network | Defender Firewall, SMB signing, WinRM HTTPS | |
| Logging | MDE sensor, Sysmon, forward to SIEM | |
| Patch | WUfB rings (0-6 days), driver blocklist |
8 Performance vs. Security Considerations
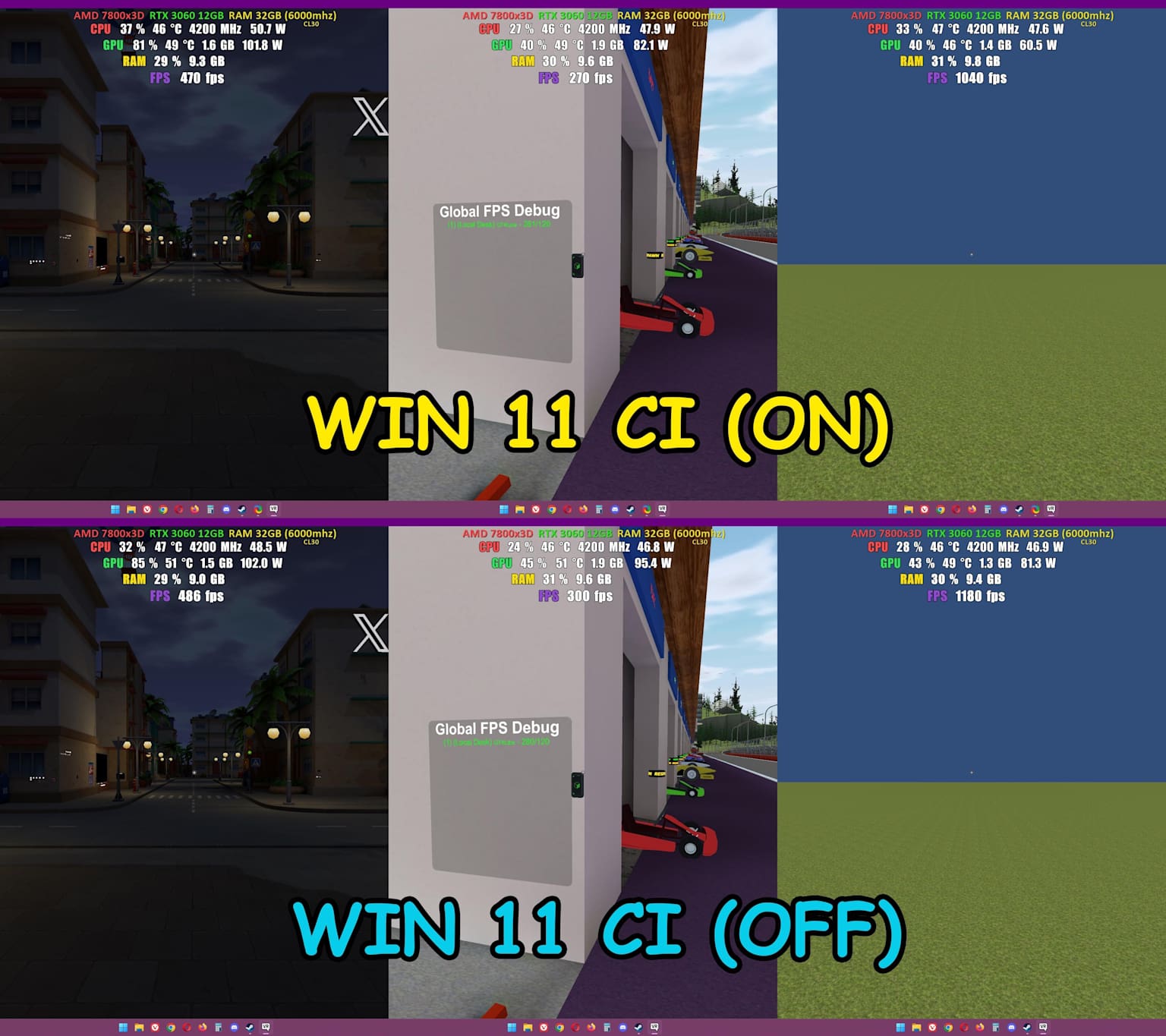
- Memory Integrity and Core Isolation can reduce gaming FPS by ≤15%; maintain two Intune rings (Workstations vs. CAD/Media labs) to balance risk.
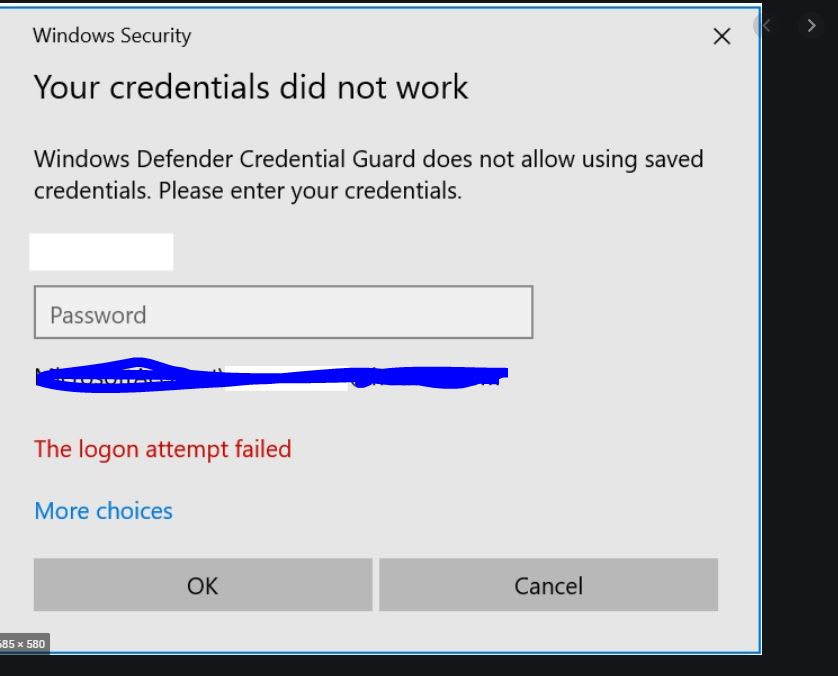
Credential Guard blocks cached credentials for RDP; educate staff and modify connection workflows.
9 Implementation Strategy
Assess current estate with CIS-CAT/MDI baseline report; score against CIS Windows 11 v4.0.0 controls.
Pilot VBS/ASR on 10% of devices; monitor Defender audit events for false positives.
Enforce hardened policies via Intune Security Baseline or GPO backed by ADMX.
Document & attest compliance evidence for auditors (baseline XML, Intune reports, SIEM dashboards).
Review quarterly to incorporate new Microsoft Security Baseline releases (e.g., 24H2 Mark-of-the-Web setting).
Conclusion
By embracing Windows 11’s built-in protections and layering enterprise controls—VBS isolation, credential safeguards, exploit reduction, application allow-listing, and rigorous monitoring—organizations can achieve a compliant, resilient endpoint fleet with minimal additional tooling. Continuous validation against the evolving Microsoft security baseline and regulatory checklists ensures that hardening remains effective against modern threat actors while aligning with audit requirements.



